The Migration Has Already Been Applied to the Database Revert It and Try Again
Migration in Entity Framework Core
Migration is a mode to keep the database schema in sync with the EF Core model past preserving information.

As per the above effigy, EF Core API builds the EF Core model from the domain (entity) classes and EF Core migrations volition create or update the database schema based on the EF Core model. Whenever y'all change the domain classes, yous need to run migration to go on the database schema up to appointment.
EF Core migrations are a set of commands which you can execute in NuGet Parcel Manager Console or in dotnet Command Line Interface (CLI).
The following tabular array lists important migration commands in EF Core.
| PMC Command | dotnet CLI command | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| add-migration <migration name> | Add <migration name> | Creates a migration by adding a migration snapshot. |
| Remove-migration | Remove | Removes the terminal migration snapshot. |
| Update-database | Update | Updates the database schema based on the last migration snapshot. |
| Script-migration | Script | Generates a SQL script using all the migration snapshots. |
Adding a Migration
At the very offset time, you defined the initial domain classes. At this point, at that place is no database for your application which can store the data from your domain classes. So, firstly, you need to create a migration.
Open up the Parcel Manager Console from the menu Tools -> NuGet Packet Manager -> Bundle Manager Panel in Visual Studio and execute the following control to add a migration.
Package Managing director Console
PM> add together-migration MyFirstMigration
If you lot are using dotnet Command Line Interface, execute the following command.
CLI
> dotnet ef migrations add MyFirstMigration
In the above commands, MyFirstMigration is the name of a migration. This volition create three files in the Migrations folder of your project, as shown below.
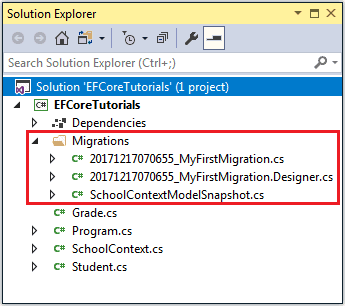
- <timestamp>_<Migration Name>.cs: The principal migration file which includes migration operations in the Up() and Down() methods. The Upward() method includes the code for creating DB objects and Downwards() method includes code for removing DB objects.
- <timestamp>_<Migration Name>.Designer.cs: The migrations metadata file which contains information used by EF Core.
- <contextclassname>ModelSnapshot.cs: A snapshot of your current model. This is used to make up one's mind what changed when creating the next migration.
Now, after creating a migration snapshot, it's fourth dimension to create the database.
Creating or Updating the Database
Use the post-obit command to create or update the database schema.
Packet Director Panel
PM> Update-Database
CLI
> dotnet ef database update
The Update command will create the database based on the context and domain classes and the migration snapshot, which is created using the add-migration or add together command.
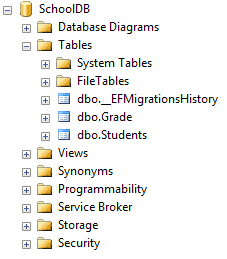
If this is the offset migration, then information technology will too create a table called __EFMigrationsHistory, which will store the name of all migrations, as and when they will be applied to the database.
Removing a Migration
You lot tin remove the concluding migration if it is not applied to the database. Employ the following remove commands to remove the final created migration files and revert the model snapshot.
Package Director Console
PM> remove-migration
CLI
> dotnet ef migrations remove
The above commands will remove the last migration and revert the model snapshot to the previous migration. Please note that if a migration is already applied to the database, so it will throw the post-obit exception.
The migration <migration name> has already been applied to the database. Revert information technology and try again. If the migration has been applied to other databases, consider reverting its changes using a new migration.
Reverting a Migration
Suppose you changed your domain grade and created the 2d migration named MySecondMigration using the add-migration command and practical this migration to the database using the Update command. Just, for some reason, you desire to revert the database to the previous country. In this example, employ the update-database <migration name> control to revert the database to the specified previous migration snapshot.
Package Manager Console
PM> Update-database MyFirstMigration
CLI
> dotnet ef database update MyFirstMigration.
The above command volition revert the database based on a migration named MyFirstMigration and remove all the changes applied for the second migration named MySecondMigration. This will also remove MySecondMigration entry from the __EFMigrationsHistory table in the database.
Note: This volition not remove the migration files related to MySecondMigration. Utilise the remove commands to remove them from the project.
Generating a SQL Script
Apply the post-obit command to generate a SQL script for the database.
Package Manager Console
PM> script-migration
CLI
> dotnet ef migrations script
The above script command will include a script for all the migrations by default. You can specify a range of migrations by using the -to and -from options.
Source: https://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/efcore/entity-framework-core-migration.aspx
0 Response to "The Migration Has Already Been Applied to the Database Revert It and Try Again"
Post a Comment